Contents
The United Nations defines Western Africa as the following 16 countries and one territory:
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Cabo Verde (Engish name: Cape Verde)
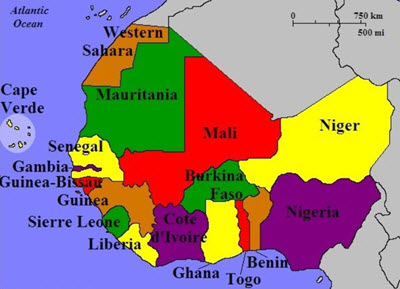
- Côte d’Ivoire (English name: Ivory Coast)
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Liberia
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha (This is a United Kingdom Overseas Territory)
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- Togo
Notably, the north-western African region Maghreb is not considered a part of Western Africa, since it is counted as a part of North Africa instead. The Maghreb consists chiefly of the countries Algeria, Morocco, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania, plus disputed territories of Western Sahara and the disputed cities Melilla and Ceuta.
Short facts about Western Africa
- Total GDP (PPP) in 2013 exceeded 750,000 USD
- The GDP per capita in 2013 was approximately USD 2,500
- Western Africa stretches over two time zones: UTC +0 and UTC +1.
Trade and currency
Most of the west African countries have their own national currencies that are used on their domestic market. Most of these currencies are small and see very little trade on the international currency market. There is one exception from this, the Nigerian Naira (NGN). The Naira sees a decent amount of trade on the currency markets and is a popular choice among African traders. The currency is the most traded African currency but nowhere as big as major currencies such as the USD, GBP, CHF, JPY, EUR, AUD or CAD. The value of the Naira has gone down sharply during the last years and we do not recommend keeping funds in this currency. Convert it into a major currency such as USD as soon as possible and only get Naira when you need it.
A large percentage of large business transactions in the region is completed in USD. This is especially true with regards to international trade. It is rare that you need local currency to do business in the area.
Popular types of trading
Forex trading
Forex trading, short for “foreign exchange trading,” involves buying and selling currencies against one another with the aim of making a profit. It’s the world’s largest financial market, where currencies are traded in pairs (e.g., EUR/USD or GBP/JPY). Traders speculate on the price movements of currency pairs, hoping to benefit from fluctuations in exchange rates.
CFD trading
CFD trading, or “Contract for Difference” trading, involves speculating on the price movement of financial instruments without actually owning the underlying asset. A CFD is a contract between a trader and a broker to exchange the difference in value of an asset from the time the contract is opened to when it is closed. It allows traders to benefit from price movements in stocks, indices, commodities, and more, without owning the actual asset. Profits or losses are realized based on the difference between the opening and closing prices of the traded instrument.
Stock trading
Stock trading involves buying and selling shares of publicly traded companies with the aim of making a profit. When you buy shares of a company, you are purchasing a piece of ownership in that company. The value of these shares can go up or down based on various factors, including the company’s financial performance, market demand, and broader economic conditions. Traders and investors aim to buy stocks at a low price and sell them at a higher price to make a profit. Stock trading can occur on stock exchanges, like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the Nasdaq, or through over-the-counter (OTC) markets.
Day trading
Day trading refers to the practice of buying and selling financial instruments, such as stocks, forex, or commodities, within the same trading day. The goal is to capitalize on short-term price movements. Day traders typically close out all positions by the end of the trading day, avoiding holding positions overnight to minimize the risk from adverse price gaps between one day’s close and the next day’s open. Due to its speculative nature and the potential for rapid gains (or losses), day trading requires a deep understanding of the markets, a solid trading strategy, and strict discipline.
ECOWAS

The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) is an organization of West African states which aims to promote the economy of the region. It was established by the 1975 Treaty of Lagos.
ECOWAS includes two sub-regional blocs:
- The West African Economic and Monetary UnionThis union is comprised of eight, mainly French-speaking states within the ECOWAS. They share a currency union and a customs union. Established in 1994, the union is commonly known by its French acronym EUMOA. All the EUMOA countries use the West African CFA franc as their currency. (ISO 4217 code: XOF). The CFA franc is pegged to the Euro. The EUMOA members are Benin, Burkina Faso, Côte d’Ivoire, Guinea-Bissau, Mali, Niger, Senegal, and Togo.
- The West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ)This group is comprised of six countries within the ECOWAS. Formed in 2000, the group members have been working to adopt their own common currency (suggested name: Eco), but as of 2019, the adoption has not yet happened.
The founding WAMZ countries are Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Nigeria, and Sierra Leone. Liberia joined in 2010. Except for Guinea, all these countries are mainly English-speaking.
History
The history of Western Africa is commonly divided into five major eras:
- First era: Prehistory: This is when the first human settlers arrived to the region and started growing foods here. Even as early as this, they were in contact with the peoples to the north.
- Second era: Iron Age: During the Iron Age, several empires consolidated both intra-Africa and extra-Africa. Centralized states developed.
- Third era: Major polities: Major polities flourished in Western Africa and had extensive contacts with non-Africans.The First Atlantic system of slave trade on a significant scale from Africa to European colonies in South America started in the early 1500s.
- Fourth era: European colonialism: Great Britain and France, respectively, colonized almost the entire region.
- Fifth era: Independence: Following World War II, nationalist movements grew across West Africa. The first sub-Saharan colony to achieve independence was Ghana, which became independent in 1957. By 1974, all the nations in Western Africa had become independent nations. (Although Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha is still a United Kingdom Overseas Territory, and the cities Melilla and Ceuta are disputed cities.)Since the end of colonialism, the economy of many West African countries and regions have suffered due to political instability, war, and violent conflicts. Examples of devastating civil wars that have plagued the region are the Nigerian Civil War, the first and second Liberian Civil Wars, the Ivorian Civil War, the Guinea-Bissau Civil War, and the Sierra Leone Civil War. Both Ghana and Burkina Faso has gone through military coups.
